Bridge Tables
Bridge tables are query assistant tables that are part of the Business Vault. Similar to PIT tables, their purpose is to improve performance of queries on the Raw Data Vault by reducing the number of required joins for such queries to simple equi-joins. A Bridge table spans across a Hub and one or more associated Links.
This means that it is essentially a specialised form of Link table, containing hash keys from the Hub and the Links its spans. It does not contain information from Satellites, however, it may contain computations and aggregations (according to grain) to increase query performance upstream when creating virtualised data marts. Bridge tables provide a timeline for valid sets of Hub and Link relationships for a given set of dates described in an As of Date table.
Below, is a diagram showing Effectivity Satellites, Hubs and Links which would be spanned by a Bridge table:
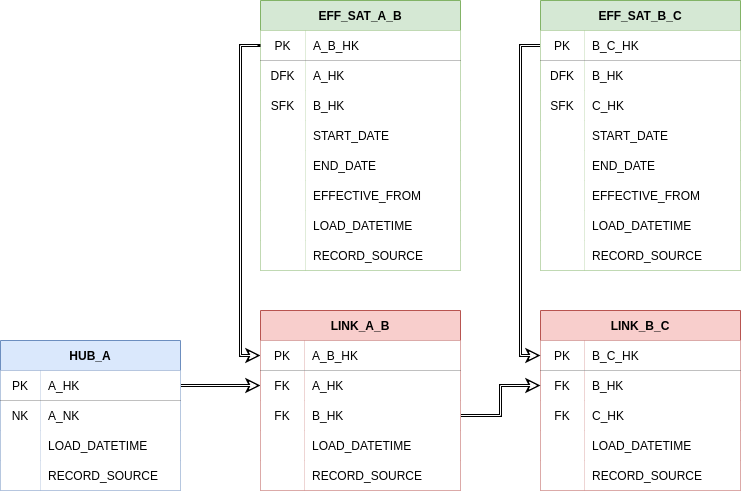
Structure¶
Our Bridge structures will contain:
Hub Table Name (source_model)¶
This is the name of the Hub that contains the primary key (src_pk) and to which the Links are connected to.
Primary Key (src_pk)¶
A primary key (or surrogate key) which is usually a hashed representation of the natural key. This will be the primary key used by the Hub.
As of Date Table (as_of_dates_table)¶
The As of Date table describes the history needed to construct the Bridge table as a list of dates. This is where you would supply the name of your As of Date table.
Bridge Table Parameters (bridge_walk)¶
This is a dictionary of Bridge table metadata subdivided into dictionaries for each link relationship. The metadata for each link relationship includes Bridge table column aliases (bridge_x), Link table name and foreign key column names (link_x), and the related Effectivity Satellite table details (eff_sat_x).
Stage Load Date Timestamps (stage_tables_ldts)¶
List of stage table load date timestamp columns. These are used to find the water-level, i.e. the latest date that hasn't yet been impacted by the stage table.
Hub Load Date Timestamp (src_ldts)¶
Hub load date timestamp column. This is used to distinguish new key relationships when compared to the water-level.
Creating Bridge models¶
Create a new dbt model as before. We'll call this one bridge_customer_order.
1 2 3 4 5 | |
To create a Bridge model, we simply copy and paste the above template into a model named after the Bridge table we are creating. AutomateDV will generate a Bridge table using parameters provided in the following steps.
Materialisation¶
Bridge tables should use the bridge_incremental materialisation, as the Bridge is remade with each new As of Date table.
Adding the metadata¶
Let's look at the metadata we need to provide to the bridge macro.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| source_model | hub_customer |
| src_pk | CUSTOMER_PK |
| src_ldts | LOAD_DATETIME |
| as_of_dates_table | AS_OF_DATE |
| satellites | {'CUSTOMER_ORDER': |
| {'bridge_link_pk': 'LINK_CUSTOMER_ORDER_PK', | |
| 'bridge_end_date': 'EFF_SAT_CUSTOMER_ORDER_ENDDATE', | |
| 'bridge_load_date': 'EFF_SAT_CUSTOMER_ORDER_LOADDATE', | |
| 'link_table': 'LINK_CUSTOMER_ORDER', | |
| 'link_pk': 'CUSTOMER_ORDER_PK', | |
| 'link_fk1': 'CUSTOMER_FK', | |
| 'link_fk2': 'ORDER_FK', | |
| 'eff_sat_table': 'EFF_SAT_CUSTOMER_ORDER', | |
| 'eff_sat_pk': 'CUSTOMER_ORDER_PK', | |
| 'eff_sat_end_date': 'END_DATE', | |
| 'eff_sat_load_date': 'LOAD_DATETIME'}, | |
| 'ORDER_PRODUCT': | |
| {'bridge_link_pk': 'LINK_ORDER_PRODUCT_PK', | |
| 'bridge_end_date': 'EFF_SAT_ORDER_PRODUCT_ENDDATE', | |
| 'bridge_load_date': 'EFF_SAT_ORDER_PRODUCT_LOADDATE', | |
| 'link_table': 'LINK_ORDER_PRODUCT', | |
| 'link_pk': 'ORDER_PRODUCT_PK', | |
| 'link_fk1': 'ORDER_FK', | |
| 'link_fk2': 'PRODUCT_FK', | |
| 'eff_sat_table': 'EFF_SAT_ORDER_PRODUCT', | |
| 'eff_sat_pk': 'ORDER_PRODUCT_PK', | |
| 'eff_sat_end_date': 'END_DATE', | |
| 'eff_sat_load_date': 'LOAD_DATETIME'}} | |
| stage_tables_ldts | {'STG_CUSTOMER_ORDER': 'LOAD_DATETIME', |
| 'STG_CUSTOMER_PRODUCT': 'LOAD_DATETIME'} |
Source table¶
Here we will define the metadata for the source_model. We will use the HUB_CUSTOMER that we built before.
1 2 3 | |
Source columns¶
Next we need to choose which source columns we will use in our BRIDGE_CUSTOMER_ORDER:
-
The primary key of the parent Hub, which is a hashed natural key. The
CUSTOMER_PKwe created earlier in the Hub section will be used forBRIDGE_CUSTOMER_ORDERas the origin Primary Key. -
LOAD_DATETIMEcolumn which represents the load date timestamp theCUSTOMER_PKis valid for.
1 2 3 4 5 | |
As of Date Table¶
The As of Date table is the source information of the As of Dates. This will provide the dates for which to generate the Bridge table.
Here we name our As of Date table AS_OF_DATE.
1 2 3 4 5 6 | |
Bridge table parameters (bridge_walk)¶
Finally, we need to choose which Links to incorporate in our BRIDGE_CUSTOMER_ORDER.
Below there are described the different Bridge aliases, Links table and column names, Effectivity Satellite table and column names associated with one of the Link - Effectivity Satellite pair (CUSTOMER_ORDER).
- The
LINK_CUSTOMER_ORDER_PKwill be the alias for the Primary Key column of theLINK_CUSTOMER_ORDERLink inside theBRIDGE_CUSTOMER_ORDERtables. - The
EFF_SAT_CUSTOMER_ORDER_ENDDATEis the Bridge alias for theEND_DATEcolumn ofLINK_CUSTOMER_ORDERLink. - The
EFF_SAT_CUSTOMER_ORDER_LOADDATEis the Bridge alias for theLOAD_DATEcolumn ofLINK_CUSTOMER_ORDERLink. - The full table name of the Link connecting the Customer and Order Hubs is
LINK_CUSTOMER_ORDER. - The name of the Primary Key column of
LINK_CUSTOMER_ORDERisCUSTOMER_ORDER_PK. - The first Foreign Key is
CUSTOMER_FK. - The second Foreign Key is
ORDER_FK. - The full table name of the associated Effectivity Satellite is
EFF_SAT_CUSTOMER_ORDER. - The Primary Key of the
EFF_SAT_CUSTOMER_ORDERtable is the same as of the parent link:CUSTOMER_ORDER_PK - The name of the column inside the
EFF_SAT_CUSTOMER_ORDERtable describing the timestamp when aCUSTOMER_ORDERrelationship ended isEND_DATE. - The name of the column inside the
EFF_SAT_CUSTOMER_ORDERtable recording the load date/timestamp of aCUSTOMER_ORDERrelationship isLOAD_DATE.
In a similar fashion, continue defining the different aliases for the ORDER_PRODUCT Link and Effectivity Satellite columns.
The dbt_project.yml below only defines two Link relationships but to add others you would follow the same method inside
the bridge_walk metadata. For instance, it can be seen where the PRODUCT_COMPONENT relationship metadata would begin.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 | |
Stage metadata¶
Finally, we add the Links & Effectivity Satellites stage table names and their Load Date/Timestamp column name.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 | |
In the end, our model should look like the following:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 | |
Running dbt¶
In order to finalise the creation of the bridge_customer_order table we use the following dbt command:
dbt run -s +bridge_customer_order
The resulting Bridge table should look like this:
| CUSTOMER_PK | AS_OF_DATE | LINK_CUSTOMER_ORDER_PK | LINK_ORDER_PRODUCT_PK |
|---|---|---|---|
| ED5984... | 2018-06-01 00:00:00.000 | A77BA1... | 8A2CQA... |
| . | . | . | . |
| . | . | . | . |
| M67Y0U... | 2018-06-01 12:00:00.000 | 1FA79C... | BH5674... |

