Creating the stage layers
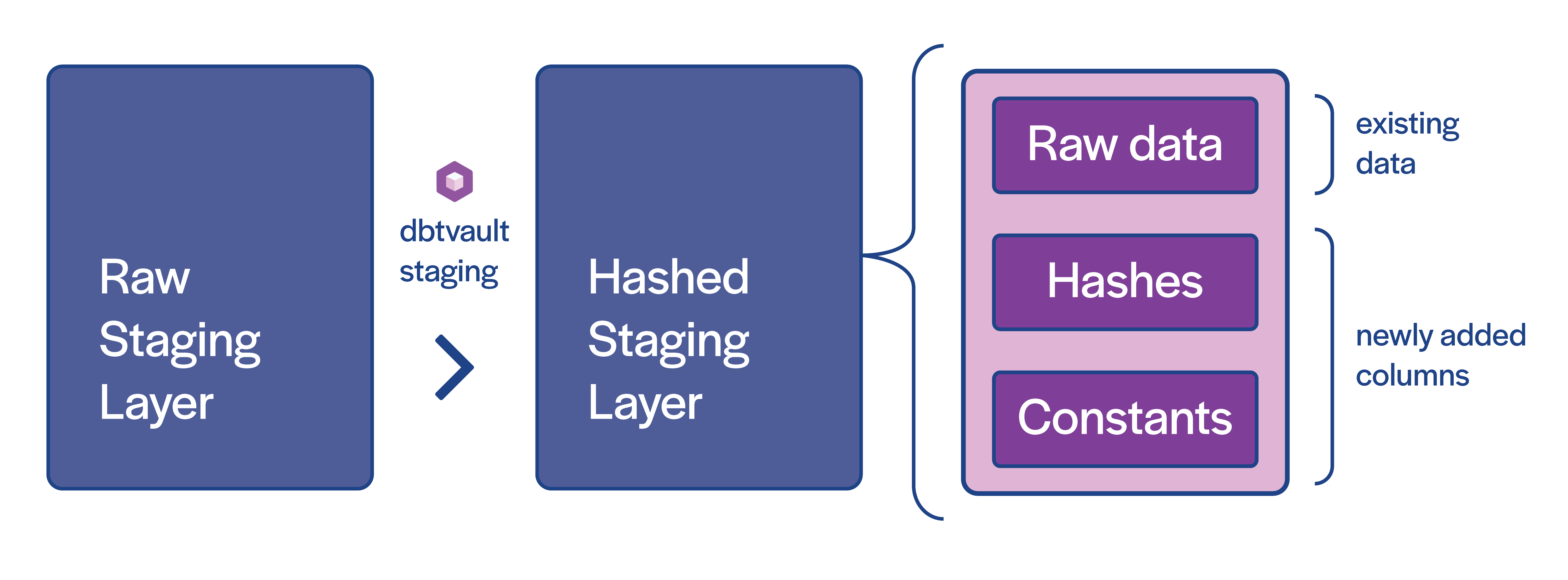
We have two staging layers, as shown in the diagram above.
The raw staging layer¶
First we create a raw staging layer. This feeds in data from the source system so that we can process it
more easily. In the models/raw folder we have provided two models which set up a raw staging layer.
raw_orders¶
The raw_orders model feeds data from TPC-H, into a wide table containing all the orders data
for a single day-feed. The day-feed will load data from the day given in the date var.
raw_inventory¶
The raw_inventory model feeds the static inventory from TPC-H. As this data does not contain any dates,
we do not need to do any additional date processing or use the date var as we did for the raw orders data.
The inventory consists of the PARTSUPP, SUPPLIER, PART and LINEITEM tables.
raw_transactions¶
The raw_inventory simulates transactions so that we can create Transactional Links. It does this by
making a number of calculations on orders made by customers and creating transaction records.
Building the raw staging layer¶
To build this layer with AutomateDV, run the below command:
dbt run --models tag:raw
dbt run -s tag:raw
Running this command will run all models which have the raw tag. We have given the raw tag to the
two raw staging layer models, so this will compile and run both models.
The dbt output should give something like this:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | |
The 'prepared' staging layer¶
The tables in the raw staging layer need additional columns to prepare the data for loading to the raw vault.
Specifically, we need to add primary key hashes, hashdiffs, and any implied fixed-value columns (see the diagram at the top of the page).
We have created a helper macro for AutomateDV, to make this step easier; the stage macro, which generates derived and hashed columns from a given raw staging table.
v_stg_orders and v_stg_inventory¶
The v_stg_orders and v_stg_inventory models use the raw layer's raw_orders and raw_inventory
models as sources, respectively. Both are created as views on the raw staging layer, as they are intended as
transformations on the data which already exists.
Each view adds a number of primary keys, hashdiffs and additional constants for use in the raw vault.
v_stg_transactions¶
The v_stg_transactions model uses the raw layer's raw_transactions model as its source
Using the stage macro¶
By using the below template and providing the required metadata, the stage macro generates hashed columns, derived columns and automatically selects all columns from the source table.
1 2 3 4 5 6 | |
Let's take a look at some metadata supplied to the stage macro for the v_stg_transactions view:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 | |
source_model¶
The source_model defines the raw stage raw_transactions which our staging layer will use to extract data from and
prepare the data for the raw vault.
derived_columns¶
We can define any additional inferred, fixed value and calculated columns using the derived_columns configuration.
1 2 3 4 | |
Here, we are creating three new columns, which are all metadata columns required for auditability in the raw vault.
-
RECORD_SOURCEis defined as a constant by prefixing the constant value with!. This is syntactic sugar to inform AutomateDV to treat this value as a constant string and not a column name. -
LOAD_DATEis defined as a calculated column using a function. Here we are synthetically creating aLOAD_DATEfor the purposes of simulating a transaction feed as described earlier in this guide. -
EFFECTIVE_FROMis our business effective date for a given record, and it makes sense to derive this from theTRANSACTION_DATE.
hashed_columns¶
Next, we define our hashed_columns.
1 2 3 4 5 6 | |
-
We are defining
TRANSACTION_HKas a new hashed column, which is formed from the concatenation of theCUSTOMER_IDandTRANSACTION_NUMBERcolumns present in theraw_transactionsmodel. -
CUSTOMER_HKandORDER_HKare both hashed from single columns, so we provide a single string with the column name.
In the v_stg_orders view we can also see an example of a hashdiff column, CUSTOMER_HASHDIFF:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | |
These work very similarly to multi-column hashes (like TRANSACTION_HK) except that we provide an is_hashdiff flag
with the value true and provide the list of columns under a columns key.
Defining a hashdiff using this syntax will ensure the columns are automatically alpha-sorted, which is standard practice for hashdiffs
Tip
For more detail on AutomateDV's hashing process, why we hash, and the differences between hash keys and hashdiffs, read more.
Deploying the 'prepared' staging layer¶
To build this layer with AutomateDV, run the below command:
dbt run --models +tag:stage
dbt run -s +tag:stage
Running this command will run all models which have the stage tag. We have given the stage tag to the
two hashed staging layer models, so this will compile and run both models.
The dbt output should give something like this:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | |

